Sometimes “greed breaks the bag”, it could not be said better. Here, the capacity of synthesis is a good advisor and less is more. And it is often enough with segmented information about your user, instead of the complete detail of all the information, although let’s take it in parts. In this article, we will see what data is important for Marketing Cloud.
If we want to simplify, we will say that we will need all the useful information to segment and personalize.
For many it will be almost everything, but in fact it usually isn’t. For example, instead of loading the entire sales history, it is much more useful to load sales totals. One scenario would be to load only the purchases by category, by user and date (month-year). This would result in far fewer lines and, in most cases, the process would be just as efficient.
Create your database ecosystem
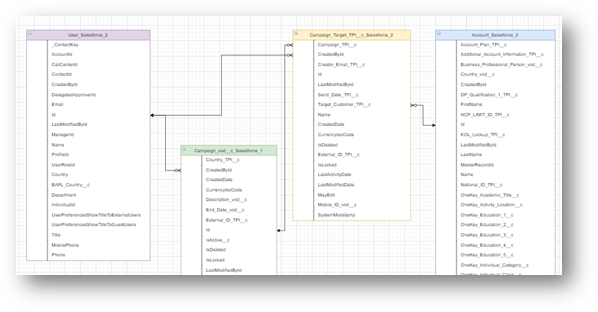
Once you have defined the objects or tables that you are going to create to support your automation strategy, it is time to get down to the concrete (we will see how you can define, within Contact Builder and there in Data Designer, all this logical data structure).
You can start defining the database structure, with the help of a software that allows you to design it (draw.io is a tool that can help you).
You will have to start defining:
- Objects or tables: specify which tables are needed. The master table, main and auxiliary tables, etc. You will probably create everything with Data Extensions. There are sendable (the ones you use to send), but all the auxiliary ones (not for sending), will be non sendable. In the case of the sendable ones, you must have the subscriber key related to all subscribers (a unique id is preferable to an email).
- Fields: define which fields will be needed. Describing them is a good tip, especially when working in a team.
Field types
It is very important to define well the fields to use, in particular, do not forget to always put the field containing the recipient’s email address as email address. Otherwise, if he/she is not registered in all subscribers, the emails will not be sent and you will get a not very pleasant surprise.
Let’s see here in detail the types of fields that exist for Data Extension in Marketing Cloud:
Text
- Can be a combination of letters, numbers and/or spaces.
- Up to 4,000 characters.
- Text field definitions can only be updated to increase the field size.
Number
- It is for integer values.
- The range of values is from: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,648.
Date
-
This date field is stored in the format MM/DD/YYYYYY.
-
It can include hours and minutes, in which case the format would be: MM/DD/YYYYYY HH:MM AM/PM.
-
When setting the System date, keep in mind that it will use the CST (Central Standard Time) system. So, depending on your target, you may have to convert it to your time zone.
-
Valid dates are those within this range: 01/01/1753 to 12/31/9999.
Boolean
-
True values: 1, Y, Yes, true.
-
False values: 0, N, No, false.
-
Accepts email addresses with correct format.
-
Maximum of 254 characters.
-
This is a required field whenever you want to use it for a sending.
Phone
-
Telephone numbers.
-
Accepts 15-digit strings and removes non-digits.
Decimal
-
Decimal values.
-
You can define the precision of the field, both integer values and number of decimals. The maximum number of positions is 38. If you define the field as 10,4 the maximum number of digits will be 10 and the maximum number of decimals will be 4. The number 123456,7890 would be valid.
Locale
-
Supports ISO language or country codes.
-
It needs a minimum of 2 characters to define a country and up to a maximum of 5 if you add the language. In the case of Spain, in Spanish it would be ES-es.
Relations
In order to define relations, you can count on different types of keys in Marketing Cloud. And for those who regularly use databases, they will be familiar.
{{cta(’52fa9c99-860e-4fbd-b8e0-8084060f20e8′,’justifycenter’)}}
“Key” types we have in Marketing Cloud
We have already thought about the necessary objects or tables and now we have to evaluate another aspect: the keys for a correct definition of our data structure.
-
Contact key: of great importance, it is the unique value you assign to identify a contact univocally in the Marketing Cloud platform. In Email Studio it is the subscriber key. It is an important decision, in cases where Salesforce CRM is connected, we will use the Record ID, which depending on the object will be: Lead ID, Contact ID and Account ID. As they are unique values, they would be our Contact KEY.
-
Primary key: this is a field with a unique key for a Data Extension. The values of the different records cannot be repeated in this field. In many cases it will be your subscriber key – contact key, but in other cases it can be a unique field for an order, etc. Normally you create a primary key, but there are tables where you may need more than one, and this is something that Marketing Cloud allows you to do.
-
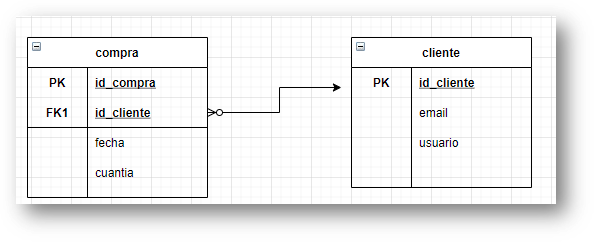
Foreign key: Marketing Cloud gives you the option of using a relational table system. In this way, what in a table is a PRIMARY KEY, when you insert it (usually from 0 to n times) is usually a FOREIGN KEY. In the previous graph we have seen a classic example, “id_cliente” is PK in the client (“cliente”) table and is Foreign Key in the table with the relation of purchases of the clients (“compra”). There (and hopefully), the customer can appear n times. Even the normal thing in that structure is that at least there is at least another relational table with the purchase lines, it means, the products, amount, value, etc. That one will have the FK of “id_compra” (purchase), as many times as items have been purchased.
And as a final tip:
-
Use a value that centralizes across the entire Marketing Cloud in Contact Builder, not one specific to a channel (such as email).
-
Logically, avoid using a value that can change over time. The best is an abstract value, such as Salesforce CRM identifiers. No DNI, email, or similar things.
-
If you have Salesforce CRM and Marketing Cloud connected, use the Lead, Contact and/or Account ID as Contact Key. This way, you can have a bidirectional communication between both tools and, in general, in all Salesforce Clouds.










